Understanding DeFi: A starter guide to decentralized finance
DeFi transforms traditional finance by replacing banks and brokers with smart contracts on blockchain networks. Discover how dapps enable lending, trading, and earning interest without intermediaries—and how Polkadot’s interoperability brings these tools together for a connected financial future.
 By Meesh Nguyen•March 25, 2025
By Meesh Nguyen•March 25, 2025
What you can expect
- Understand the evolution and differences between TradFi and CeFi to DeFi
- Learn what is DeFi and how it works
- Explore key components like smart contracts, wallets, and dapps
- Discover what you can actually do with DeFi, from trading to lending
- How Polkadot powers multichain DeFi and the future of finance with built-in interoperability
Decentralized finance, or DeFi, represents a revolutionary shift in how the global financial system operates. It is an umbrella term that refers to a growing ecosystem of decentralized applications (dapps), protocols, and platforms built on public blockchain networks that deliver financial services without the need for centralized intermediaries like traditional banks, brokerages, or payment processors.
Instead of going through centralized gatekeepers, DeFi allows users to access peer-to-peer financial services like lending, borrowing, trading, and earning interest directly. These smart contracts, written as self-executing code on blockchain networks, remove the need for third-party trust and reduce costs while increasing access and transparency.
Open-source and permissionless by design, the DeFi ecosystem empowers anyone with an internet connection to access financial tools that were previously gated by geography, bureaucracy, or capital. According to the World Bank, more than 1.4 billion people globally remain unbanked. DeFi offers them a way in.
And yet, not all DeFi is created equal. Liquidity shouldn't be locked into a single chain or siloed within one ecosystem. True permissionless finance means users can move value freely across networks. This is where platforms like Polkadot stand out, enabling interoperability and multichain DeFi that removes the barriers between otherwise fragmented protocols.
Whether you’re DeFi curious or ready to dive in, this guide will walk you through how we got here, how it works, and where it’s heading.
How did we get here?
To understand DeFi’s potential, it helps to look back at the systems it's aiming to improve.
The evolution arc from TradFi to CeFi to DeFi
For most of modern history, traditional finance (TradFi) has dominated how people store, transfer, and grow money. Banks, governments, and financial institutions act as trusted intermediaries — providing everything from loans to checking accounts. But they also control access, enforce high fees, and are prone to inefficiencies, exclusion, and even failure.
Shortly after the 2008 financial crisis, the emergence of Bitcoin introduced a radically new idea to the public: a financial system not controlled by any central authority. This spawned a decentralized revolution, inspiring a wave of technologies designed to rethink how value and data are stored online. Somewhere between TradFi and DeFi, centralized finance (CeFi) emerged—largely driven by the need for better user experience. Platforms like Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken offer ways to convert money into crypto, but CeFi still operates under centralized control. While it helped bring cryptocurrency to the mainstream, CeFi also reintroduced many of TradFi’s issues, such as limited transparency, custodial risk, and regulatory bottlenecks.
So what’s the difference?
- TradFi: Legacy financial institutions like banks and credit unions
- CeFi: Centralized crypto services that manage user funds, provide KYC/AML, and resemble banks in structure
- DeFi: Decentralized protocols built on blockchain that allow users to interact peer-to-peer without intermediaries
Is DeFi the final destination for financial freedom?
Maybe. DeFi is still evolving — and fast. While it's a powerful shift toward user-owned, permissionless finance, it’s not without challenges. Usability, education, regulation, and scalability are still very much a work in progress.
But even in its early form, DeFi represents a meaningful alternative. It’s a glimpse of what finance could become when systems are open, programmable, and accessible to everyone.
What is DeFi and how does it work?
Decentralized finance is a new way of accessing and using financial services without banks, brokers, or other intermediaries. Instead of relying on traditional financial institutions to manage your money, DeFi uses code. Specifically, it runs on public blockchain networks like Polkadot and Ethereum, where smart contracts execute financial transactions automatically and transparently.
In DeFi, there’s no bank holding your funds. Your assets are onchain and recorded on an immutable ledger tied to your public wallet address. Instead of logging into a bank account, you connect your crypto wallet. Want to trade or swap tokens? Connect to a decentralized exchange (DEX). Looking to borrow or lend? Instead of going through a loan officer, you can interact directly with a lending protocol like AAVE or Kylix Finance. Everything is peer-to-peer, with smart contracts handling the logic and execution. This lowers the barriers to who gets to participate and gives users direct control over their financial assets.
DeFi as a financial technology
DeFi is part of the broader financial technology (aka fintech) movement but differs from the apps you might use to transfer money or manage investments today. While fintech builds better user experiences on top of traditional infrastructure, DeFi operates entirely on a tech stack that's purpose-built for the open, decentralized web.
Let’s break it down:
- Traditional finance: Relies on banks, custodians, and payment processors
- Fintech: Builds sleek apps that still depend on traditional rails
- DeFi: Uses smart contracts and decentralized protocols to remove intermediaries altogether
With DeFi, users don’t need to trust an institution. They can verify the rules in the code. Every transaction is auditable. Every action is traceable. Fundamentally, it’s a shift from trust to truth.
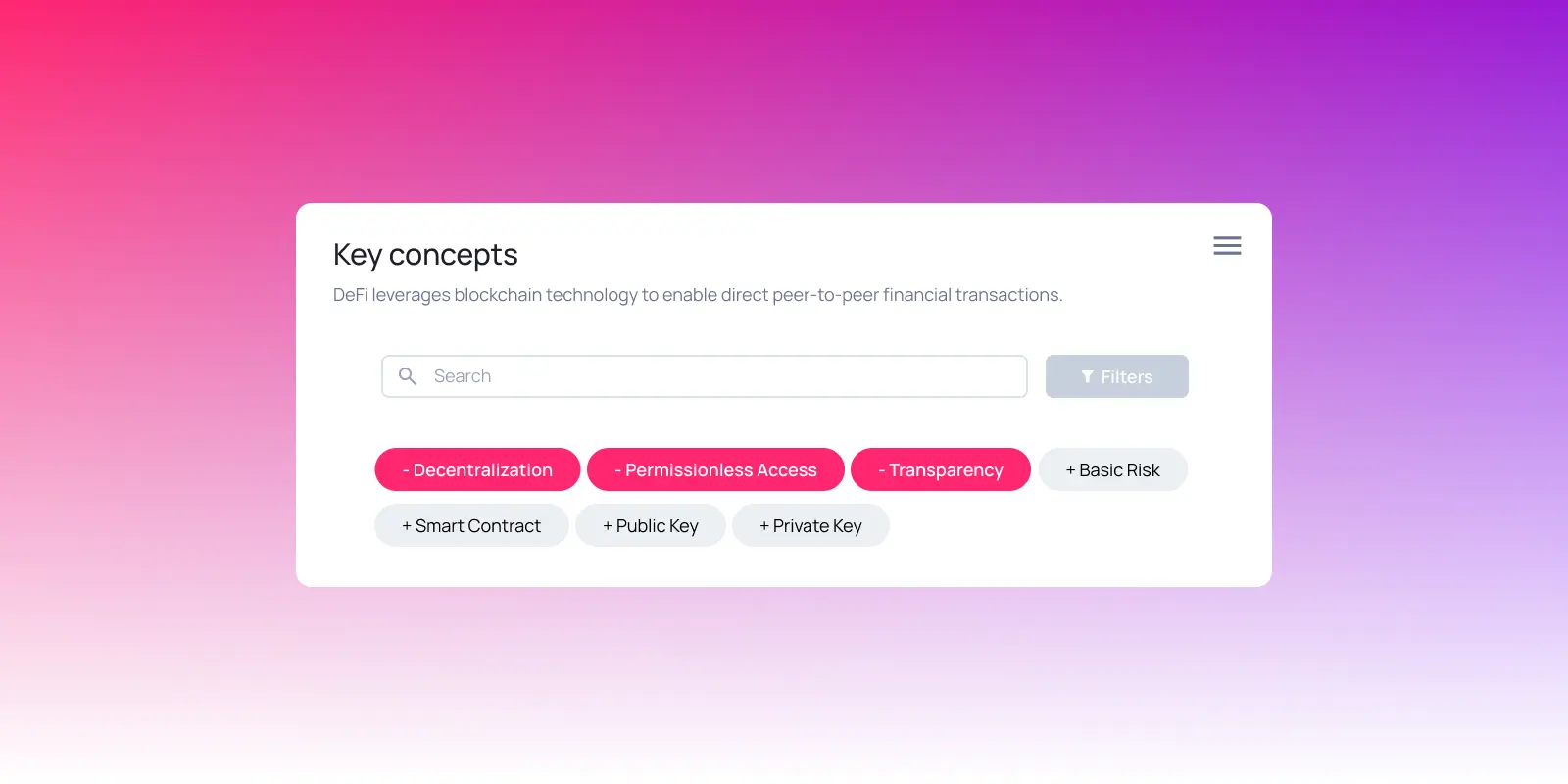
Key components that make DeFi possible
You might be wondering: do we really need blockchain technology to do this? Couldn’t we just use regular databases or distributed systems?
It’s a fair question. But blockchains are more than just distributed data storage. They provide trustless coordination, which is a way for people who don’t know or trust each other to interact financially without relying on a central authority. That’s something traditional infrastructure can’t do on its own.
The building blocks:
1. Blockchain networks: These form the foundation. DeFi operates on public networks like Ethereum and Polkadot, which provide decentralized infrastructure.
2. Smart contracts: Self-executing digital contracts written as code that defines and enforces the rules of a transaction. Once deployed, no single party can alter the contract.
3. Decentralized applications (dapps): User-facing applications that connect to smart contracts. These decentralized software programs offer access to services like swapping, trading, lending, or borrowing.
4. Crypto wallets: More than a digital wallet, but rather a crypto wallet is like an all-access pass to Web3. Wallets like MetaMask, Nova Wallet, and Phantom enable users to hold, stake, send, and receive assets while serving as a login to DeFi.
5. Public and private key cryptography: Behind the scenes, cryptography keys enable secure authentication and transaction signing, securing access to your funds and verifying your transactions.
Together, these components unlock the defining attributes of DeFi:
- Transparency: Everything happens onchain and in public.
- Permissionlessness: Anyone can use or build without approval.
- Accessibility: No gatekeepers or minimum requirements.
What can you actually do with DeFi?
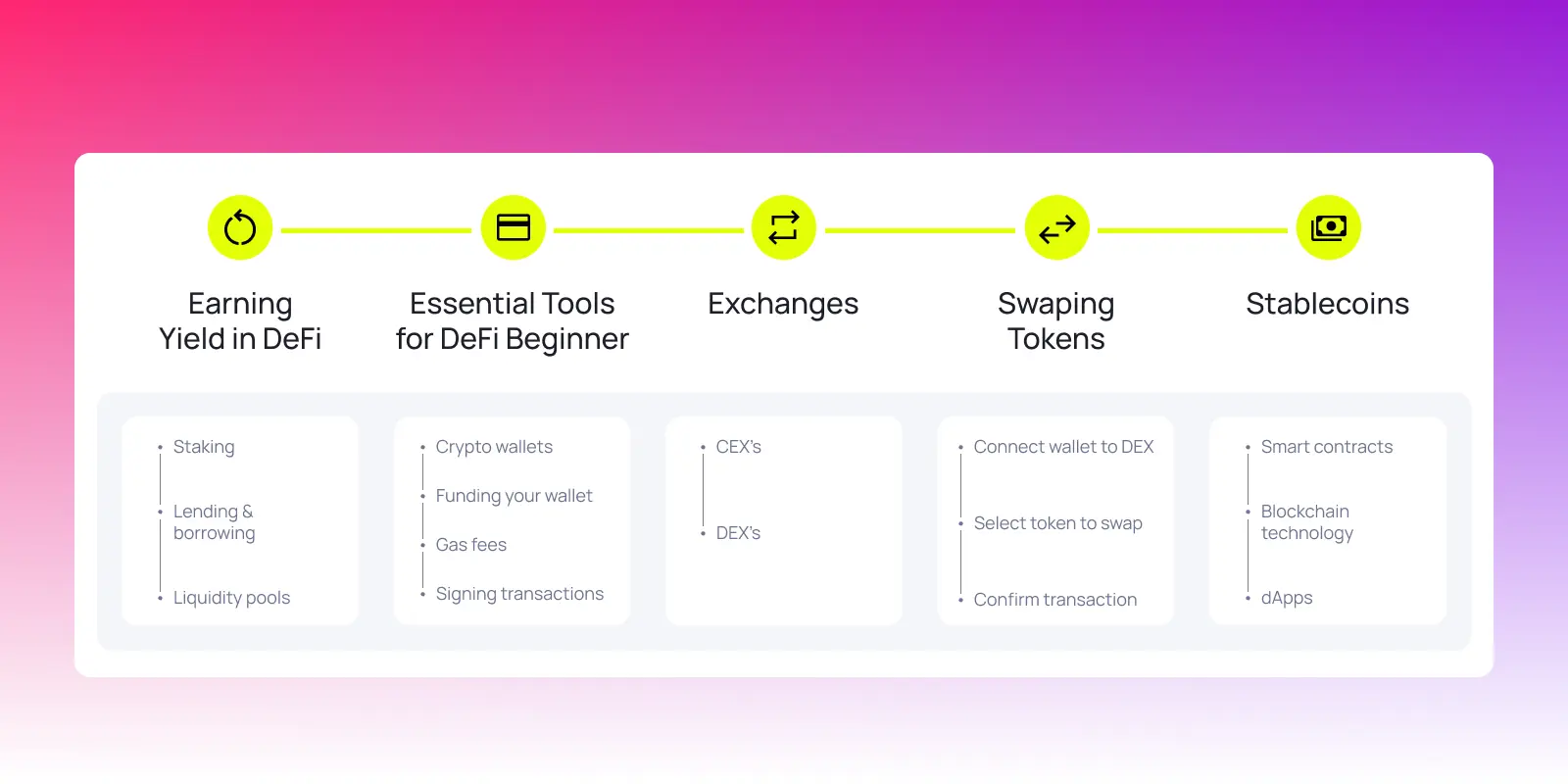
Like all technologies, its potential lies in what you can actually do with it. The DeFi ecosystem unlocks a wide range of financial activities that were once only available through banks or traditional institutions. Now, they’re accessible to anyone with a crypto wallet and an internet connection, making financial systems more efficient, inclusive, and open.
Let's explore some of the core services that define the DeFi ecosystem:
- Centralized exchanges (CEXs): Platforms like Coinbase or Kraken can help you get started before you bridge to DeFi-native platforms.
- Decentralized exchanges (DEXs): Trade tokens without a centralized exchange.
- Lending and borrowing: Supply crypto assets to earn interest or borrow by depositing crypto as collateral. All are handled by smart contracts.
- Automated market makers (AMMs) use algorithms and liquidity pools instead of order books to determine prices. Anyone can contribute assets and benefit from liquidity provisioning.
- Yield farming: Maximize returns by staking or locking tokens in DeFi protocols. High risk, high reward.
- Stablecoins: Use crypto assets pegged to fiat currencies for trading, savings, or as collateral — all while minimizing volatility.
- Peer-to-peer transactions: Send and receive crypto directly — no banks, no intermediaries.
Many of these use cases benefit from cross-chain interoperability. On Polkadot, for example, liquidity and data can flow across rollups without needing specialty bridges for each rollup, creating more efficient and safer financial workflows. Together, these services highlight how DeFi is reshaping finance, offering tools for people to participate, transact, and grow wealth on their own terms.
Why DeFi matters for users
DeFi changes the relationship between people and money. Instead of relying on financial institutions to grant access, users take control.
- You manage your assets with a self-custodied wallet
- You choose how to interact with protocols, not companies
- You don’t need permission to participate
This is especially powerful in regions where banking is inaccessible, unstable, or untrustworthy. DeFi empowers users to send and receive remittances, access loans, and earn yield — often for the first time. And with a multichain infrastructure like Polkadot, composability is baked into financial products, enabling access across networks.
Benefits and challenges of DeFi
Like any emerging technology, DeFi comes with both advantages and trade-offs. While the benefits of greater autonomy are transformative, the risks require awareness and responsible participation. Here's a balanced overview of what you can expect.
Benefits
- Transparency and trustlessness: Everything is visible onchain. Smart contracts enforce the rules.
- Open and permissionless access: DeFi is accessible to anyone with a crypto wallet and internet connection. Unlike traditional methods, it doesn’t require a lengthy sign-up process or identity verification (often called “Know Your Customer” or KYC). This lowers barriers for people around the world who may not have access to formal banking systems.
- Interoperability and composability: Protocols can plug into and build on top of each other, building a more powerful, diverse ecosystem.
- Global participation: From Lagos to London, decentralization enables anyone with a crypto wallet to participate instantly and affordably.
Potential challenges
- Regulatory uncertainty: DeFi operates in a gray zone where rules vary by jurisdiction.
- Security risks: Phishing scams, fake dapps, and lost wallet seed (recovery) phrases can lead to permanent loss of funds. Users should stay alert, verify links, and understand what they’re signing before connecting their wallet.
- Market volatility: Crypto moves fast. Sharp price swings can impact lending positions, stablecoins, or collateralized loans.
- Usability and education gaps: DeFi introduces new tools, unfamiliar terms, and a learning curve that can feel overwhelming. For newcomers used to traditional apps and banking, the onboarding experience can be confusing without clear guidance and user-friendly design.
Overview of how to get started with DeFi
Getting started with DeFi doesn't have to be overwhelming. While we’ll go deeper into step-by-step walkthroughs in future guides, here’s a high-level overview of how people typically start exploring DeFi:
1. Your onchain identity – Crypto wallets
Wallets like Nova Wallet, Zerion, or Phantom serve as your login to DeFi. Wallets are usually designed for specific blockchain environments — like EVM-compatible wallets (built for Ethereum-based dapps), PVM-compatible wallets (built for Polkadot-based dapps), or Solana wallets (built for Solana-based dapps). Unlike CeFi, where you create an account, crypto wallets are self-custodied and cryptographically secured.
2. Access points – CeFi and bridges
Even if you’re heading into DeFi, CeFi platforms like Coinbase or Kraken can be helpful for onramping or the process of converting fiat (USD, EUR) into cryptocurrency. From there, users often send funds to self-custodied wallets to interact with DeFi dapps. Projects like Hyperbridge are building fully onchain multichain bridges to allow assets and data to move securely across networks. This enables users to interact with DeFi across multiple chains without relying on centralized bridges.
3. Platforms and protocols – Where DeFi happens
Once your funds are onchain and in your wallet, you can explore DeFi applications. These include decentralized exchanges (DEXs) for trading, lending protocols to earn or borrow, staking platforms for rewards, and other dapps built around finance. Each platform runs on smart contracts, giving you full control and transparency over how you interact with your assets.
Trends and innovations shaping the future of finance
DeFi continues to evolve. Here are some of the most meaningful trends shaping where it’s headed:
- Real-world assets (RWA) and traditional integration: Tokenizing physical and financial assets like real estate, government T-bills, and bonds brings traditional assets onchain, expanding DeFi’s use cases.
- Liquid staking and restaking: Users can stake tokens and still access liquidity or even restake them across chains and dapps. Polkadot projects, like Bifrost, are creating cross-chain liquid staking experiences, enabling users seamless access to DeFi opportunities.
- Multichain and cross-chain liquidity: Polkadot and other ecosystems are solving fragmentation by enabling seamless asset movement between chains.
- DeFi 2.0 and sustainable economics: A movement toward more sustainable protocols with better tokenomics and incentive alignment, similar to Polkadot 2.0’s initiative, which focuses on aligning network incentives and lowering barriers for builders.
- Regulatory innovation: From stablecoin frameworks to decentralized identity (DIDs), regulation is gaining structure and clarity.
These trends all point to one thing: DeFi isn’t slowing down. It’s expanding in scope, sophistication, and global relevance. Already reshaping how people think about access to money, ownership, and opportunity, DeFi’s emerging as a financial system that’s more open and inclusive than anything that came before it.
As networks like Polkadot continue to enhance the core for a more interoperable DeFi ecosystem, the potential for participation and builders continues to grow. Whether you’re just starting your DeFi journey, ready to build the next wave of DeFi protocols, or just curious about potential blockchain use cases, it’s a good time to start paying attention to what’s possible.











