Decentralization’s ripple effect: How Web3 is rewriting digital sovereignty
Centralized platforms dictate access, control data, and pose security risks, leaving individuals without control over their digital presence. Decentralization offers a resilient alternative, paving the way to a digitally sovereign future.
 By Meesh Nguyen•January 31, 2025
By Meesh Nguyen•January 31, 2025
What you can expect
- The case for Web3
- How the internet centralized and why it’s time to decentralize
- Technological breakthroughs that make decentralized networks scalable
- Why decentralization matters
- The ripple effect of decentralization and Web3
Imagine waking up to find a digital service you rely on suddenly gone. Perhaps your favorite social media platform has been banned, your financial app has been hacked, or your cloud storage provider is experiencing a massive outage. It sounds like the setup for a dystopian sci-fi movie, but these disruptions are far from fictional—they are already happening.
The 2019 Cloudflare outage took down major parts of the internet, disrupting millions of websites. The TikTok bans in certain regions have restricted millions of users’ access to information and self-expression. And centralized service providers continue to collect vast amounts of personal data, leaving users vulnerable to exploitation. In a hyperconnected world where 5.5 billion people—over 68% of the global population—are internet users, such disruptions can have long-lasting consequences.
While digital services have made life more seamless, connected, and efficient, many users feel powerless over how their personal data is handled. This growing discontentment with centralized systems prompts a crucial question: Is there a better way? Could decentralized systems pave the path toward digital sovereignty in a resilient, user-owned digital future?
The case for Web3
Now imagine a different reality—one where platforms are built to be accessible, tamper-proof, transparent, and, most importantly, controlled by their community of users. Instead of relying on a single authority to oversee data, operations, and governance, decentralized systems distribute power across a global network of participants.
By design, technical decentralization enables digital sovereignty, allowing individuals and communities to govern their digital footprint without reliance on a central entity. But what does decentralization truly mean? Is it a concept, an organizational structure, or the foundation of a new technological paradigm?
How the internet centralized and why it’s time to decentralize
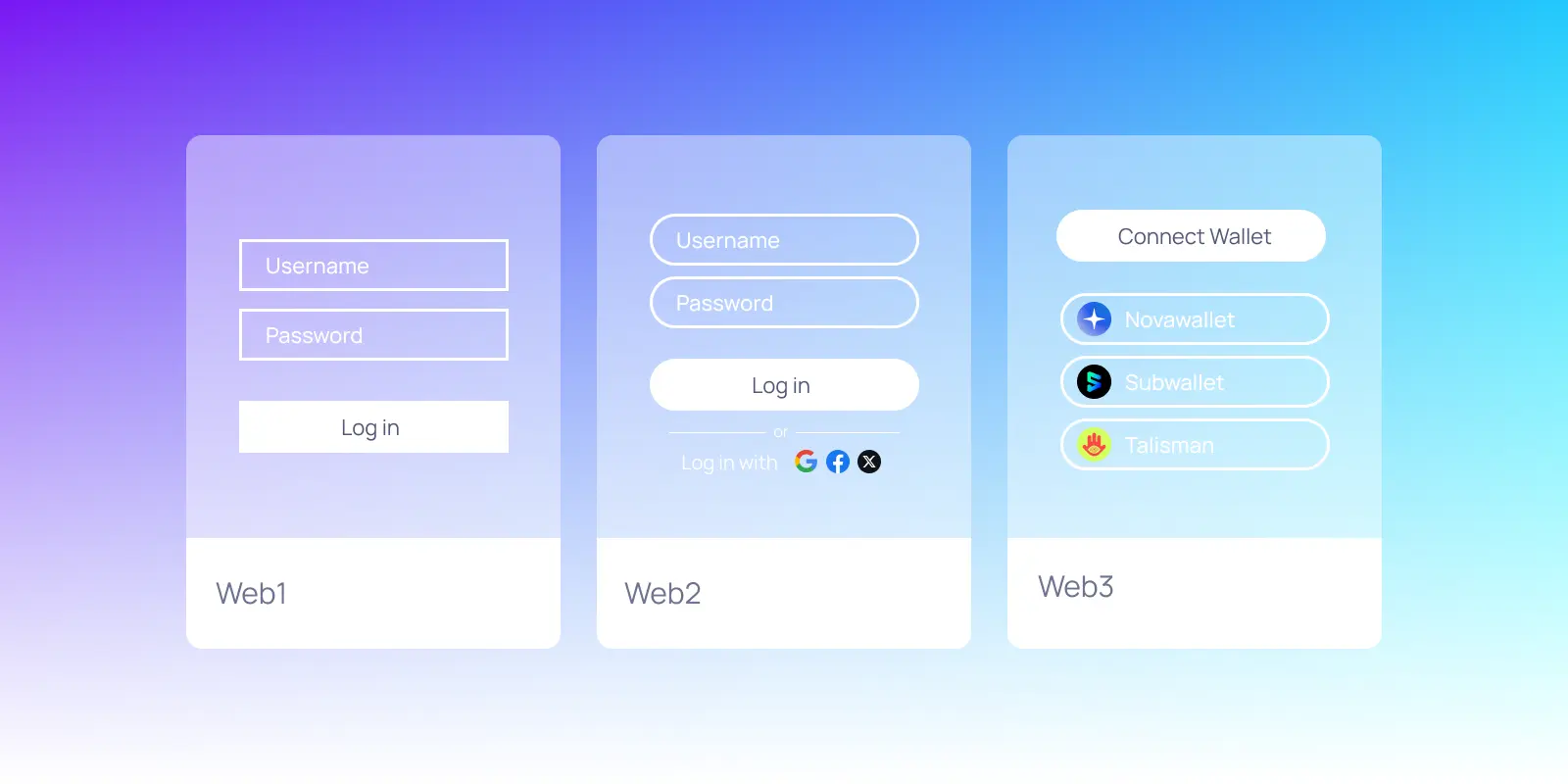
To understand the importance of decentralization, we need to revisit the history of the internet, which can be traced through three major eras: Web1, Web2, and Web3.
The early internet was built on open protocols that prioritized distribution and community governance. Individuals controlled their servers, email systems, and data, and the web operated without a centralized gatekeeping entity.
As the internet matured, centralized for-profit entities emerged, offering closed-source proprietary services that outweighed the capabilities and scale of open protocols at the time. While centralized services provided convenience, this came at a price—users’ data and online interactions were now controlled by a few corporate entities. These systems began collecting data to train algorithms and fuel ad-driven business models, raising concerns about privacy, misaligned incentives, and monopolistic control.
The rising concerns over centralized systems, marked by security vulnerabilities, data breaches, and opaque governance, sparked a movement toward decentralized, open-source networks. Bitcoin emerged from the Cypherpunk ethos in the wake of the global 2008 financial crisis that exposed systemic flaws and rampant fraudulent activity in traditional financial institutions. Coded in Bitcoin’s genesis block, Satoshi Nakamoto, the mysterious inventor of Bitcoin, included a headline from The Times:
“Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks”
Though Satoshi never explained the message’s meaning, many view it as a powerful declaration of Bitcoin’s purpose: to create a trustless, peer-to-peer electronic payment system that eliminated dependency on centralized financial systems. Since then, blockchain technology and cryptographic advancements have returned control to users, prioritizing transparency, privacy, and resilience.
Dr. Gavin Wood, Founder of Polkadot and Co-founder of Ethereum, coined the term Web3 in 2014 to encapsulate his vision of a more open, transparent, and user-centric internet ecosystem built on blockchain technology.
Technological breakthroughs that make decentralized networks scalable
Limited by scalability and usability challenges, true decentralization at scale was once more of an ideal than a reality. Recent blockchain advancements, like optimized consensus mechanisms and efficient use of block space, provided a way to cheaper and faster transactions, making decentralized systems practical at scale.
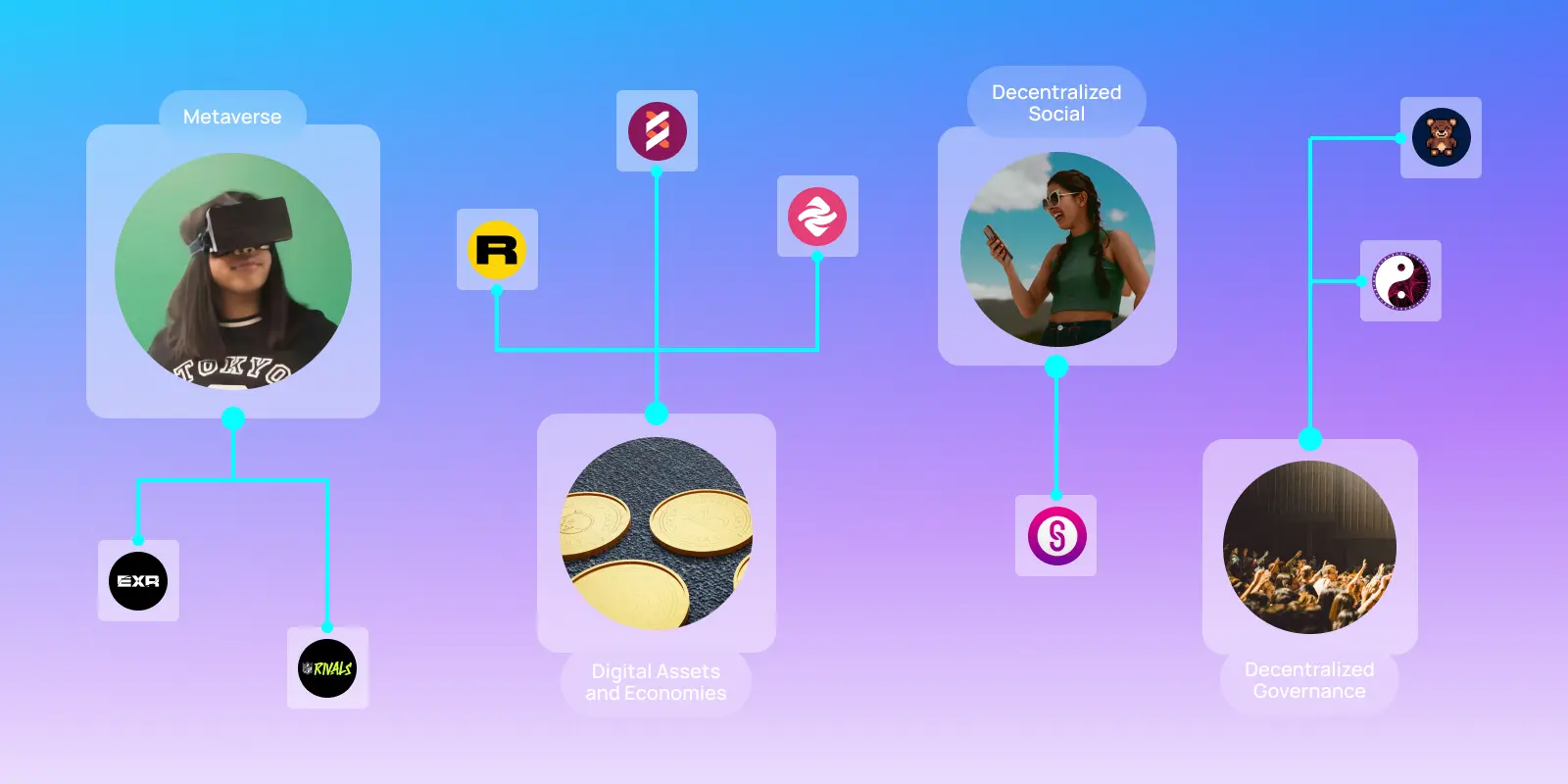
Modular, open-source blockchain networks like Polkadot exemplify this evolution by distributing transactions across a global network of independent validators and nodes. This architecture ensures both security and scalability without centralized control, giving rise to a host of decentralized applications that bring us closer to a digitally sovereign future.
Decentralized social media
Reimagined social networks like Threads and Bluesky, built using the distributed AT protocol, and Warpcast, built on the decentralized Farcaster protocol, allow users to own their data, posts, and communities, reducing the risks of censorship and algorithmic bias that plague centralized platforms.
Decentralized identity and self-sovereign identity (SSI)
Decentralized digital identity solutions like DIDs (Decentralized Identifiers) and VCs (verifiable credentials) enable users to verify their identities without exposing personal data. NFTs (non-fungible tokens) allow creators to retain ownership and prove the authenticity of their content. This fundamentally shifts ownership of online identity and privacy controls back to the user, preventing external databases from storing sensitive user information.
Decentralized finance (DeFi)
DeFi platforms like Hydration and Uniswap replace traditional financial intermediaries with permissionless protocols like automated market makers (AMM), enabling global access to financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading. For the 1.4 billion unbanked individuals worldwide, DeFi offers financial inclusion and economic empowerment.
Decentralized governance and DAOs
Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) enable transparent and trustless onchain decision-making, eliminating the need for intermediaries and empowering users with direct voting power over key decisions. In the Polkadot ecosystem, DOT token holders can participate directly in governance and vote on network-wide issues, including policies, network upgrades, and resource allocation.
Polakdot’s onchain governance protocol, OpenGov, ensures that community-approved decisions are executed autonomously without requiring oversight from a central governing entity. As the largest DAO in the world, Polkadot DAO manages a treasury worth billions, funding projects and promoting innovation through collective decision-making.
Decentralized storage solutions
Decentralized and resilient infrastructure like CESS, IPFS, Filecoin, and Arweave distribute data across decentralized nodes, preventing single points of failure and ensuring reliable protection against hacks, outages, censorship, or monopolistic data locking.
Why decentralization matters
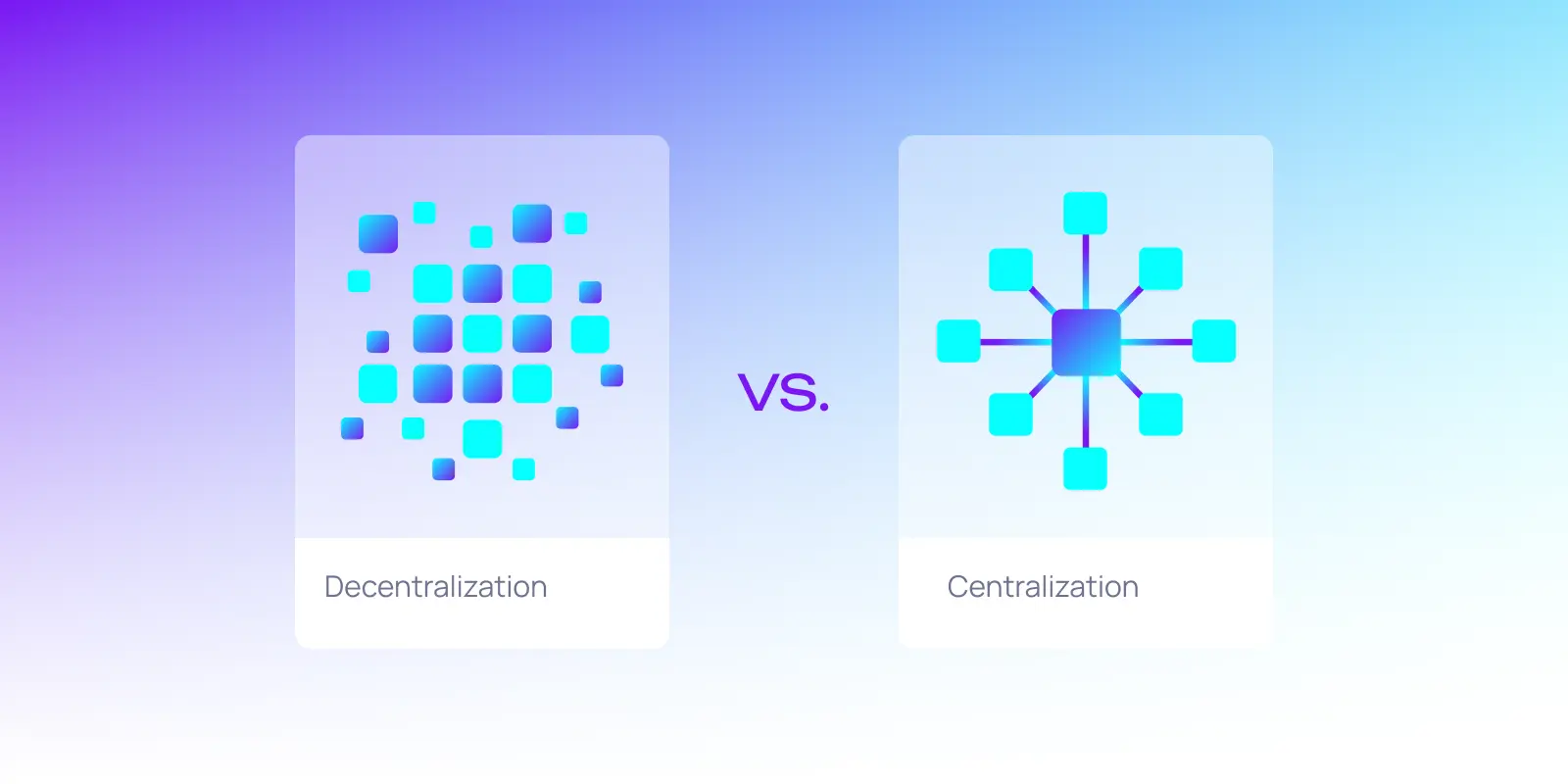
The problems of centralized systems have become undeniable. Single points of control create security vulnerabilities, opaque data practices erode privacy, and monopolistic business models stifle innovation.
Decentralization addresses these challenges by offering:
- Enhanced privacy: In decentralized systems, users can control their data, sharing only what is necessary while ensuring transactions are private and secure.
- Improved security: Blockchain technology and decentralized storage distribute data across nodes, making it nearly impossible for hackers to target a single point of failure. This reduces the risks of massive breaches like the 2017 Equifax data breach that exposed personal data, including Social Security numbers of 147 million people.
- Neutrality and fairness: Unlike centralized platforms that often prioritize profit at the expense of users, decentralized systems build fairness into their architecture, allowing users to participate in governance and directly benefit from the systems they use.
- Participatory governance: Through DAOs, users can vote on platform upgrades, rules, and resource allocation. This transparent, democratic model reduces corruption and gives participants a say in the evolution of the systems they depend on.
The ripple effect of decentralization and Web3
Decentralization is not just a technological shift; it’s a societal transformation. It redefines digital ownership, prioritizes individual privacy, and builds systems that are more resilient, inclusive, and transparent. By removing gatekeepers, decentralization redistributes control to users and communities, paving the way for a future where digital sovereignty is always the norm and never the exception. As Chris Dixon once wrote:
“Centralized platforms have been dominant for so long that many people have forgotten there is a better way to build internet services.”
It’s time to leave behind extractive centralized ecosystems and embrace a decentralized future that empowers everyone.











